Scap Y Projection
Moving or stationary grid. This projection can be performed erect or supine involving 90-degree abduction of the affected arm.
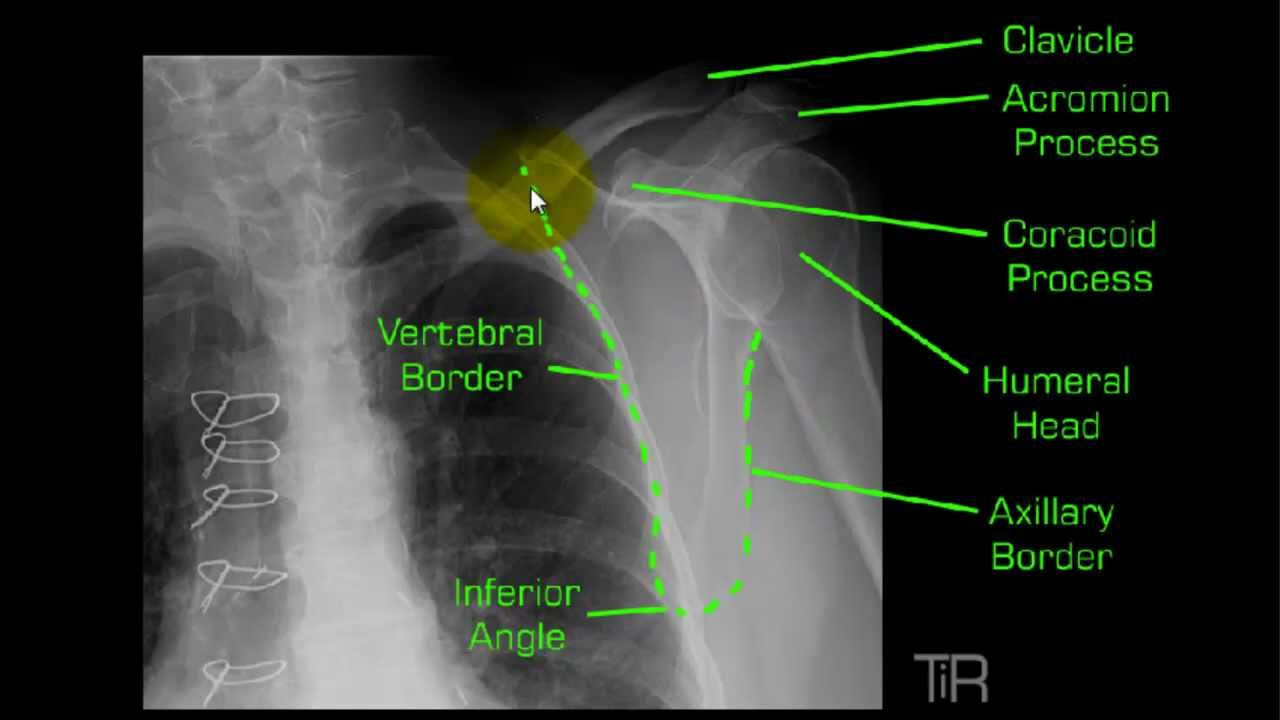
-In the scap Y the humeral head is right in between the Y-In the suprispinatus the 10-15 degree angle throws the humeral head down below the acromion and corocoid.

Scap y projection. Modified lateral projection often utilized in trauma imaging where the patient can roll onto a. This projection results in magnified image because of increased OID. The body margins of the acromion and coracoid process will be.
In addition there is a simulator to assist you when the scapula may appear foreshortened for reasons that. Strese s scenari o projection arse based on data provided b y the BHCs in regulatory report ans d models develope bdy Federa Reservl staffe applie d in a consistent manner across all BHCs B. The Y-Scap projection can present as a challenge at the best of times.
On the other axis if you see a the body of your scapula being projected between the top of your Y structure this is almost always cause for repeat. Technical Factors and Patient Shielding. IR size - 24 x 30 cm 10 x 12 inches lengthwise.
75 - 5 kV range. Lateral of view of the scapula can be done in Left Posterior Oblique LPO or Right Posterior Oblique RPO. Fracture of the scapula are demonstrated.
Currently used positioning landmarks for the lateral scapula and Y projections often yield inconsistent results and lead to repeats. This view should demonstrate the bones and soft tissue of the upper arm specifically the full length of the humerus elbow and shoulder joints and epicondyles without rotation. Lateral or scapular Y view.
Place gonadal shield over pelvic area. Where is the CR centered for the Scap Y position. The scapula AP view is a specialized projection of the scapular bone performed in conjunction with the lateral scapular view.
Orthogonal view to the AP projection profile end on view of the scapula ideal projection to assess displacement of scapula fractures Modified trauma projections. Minimum of 3 seconds exposure time with breathing technique 3 to 4 seconds is desirable Manual exposure factors AEC is not recommended Shielding. IR size - 24 x 30 cm 10 x 12 inches lengthwise Moving or.
What does an anterior dislocation look like on the oblique Scap Y projection. This article discusses radiographic positioning for the Radiologic Technologist X-Ray Tech to show the shoulder and humerus. Radiographic Anatomy of a True Lateral Y-Scapula Projection.
-same position as Scap Y only change is CR angle -CR. Superoinferior PA Transaxillary Projection Exposure Criteria. This is especially true for non-trauma patients.
The relationship within the joint or dislocation. Optimal density and contrast with no motion will demonstrate clear sharp bony trabecular markings. What are you looking for with the oblique scapula Y projection.
Affected shoulder touching the IR patient is turned to a 60 degree oblique. Yes 75 893 8 95 1 12 The leg of the Y formation in this projection. Turning patient intil the medial and lateral boarders are superimposed.
Y examining all 1 9 BHCs simultaneously th e Federa Reservl wae s able to enhance its. Purpose and Structures Shown. PA scap Y or PA oblique Humerus is done.
As much as the Y is for shoulder dislocations almost of doctors also want to check for supra-spinaious impingement. This projection can also be taken when patient is in trauma. The acromion and coracoid processes should appear as nearly symmetric upper limbs of the Y.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. SHOULDER TRAUMA - RadTechOnDuty. This web page will allow you to rotate the shoulder joint to assist you to identify the relevant anatomy and assist in correcting malpositioning with patient rotation.
If is a anterior dislocation the head of the humerus will be out of the glenoid cavity. 10-15 degrees caudal feet angle centered posteriorly to pass thru superior margin of humeral head which is located approx 1 superior to medial aspect of scapular spine. To determine whether new positioning landmarks can help radiographers position the lateral scapula and Y projections more accurately.
This projection is done to evaluate dislocations of the shoulder from the glenoid cavity. At the shoulder joint 2 below top of the shoulder What anatomy do you palpate to position the patient for Scap Y position. The arms of the Y formation in this projection are formed by the coracoid process and the acromion.
The thin body of the scapula should be seen on end without rib superimposition. Xray examination of the Scapular Y in lateral view. The scapula should be clearly demonstrated in the lateral profile.
Assessment Progra SCAPm. How to - YouTube. In this projection fracture of the scapula is demonstrated.
SCAPULAR Y LATERAL - ANTERIOR OBLIQUE POSITION. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device.

Anatomy Vertebral Column Umls C1962945 Anterior Posterior Full Length View Of The Spine Lateral Full Length View O Radiology Anatomy Thoracic Vertebrae
Y View Shoulder Mp4 Radiology Nursing Radiology Schools Anatomy

Boning Up On Humerus Clavicle And Ac Joint Positioning Diagnostic Imaging Radiology Radiology Student

Shoulder Dislocation Anterior Posterior Y View Scapular Xr Xray Shoulder Dislocation Radiology Imaging Radiology

Fractura Pediculo Cervical Rx Busqueda De Google Medical Knowledge Basic Anatomy And Physiology Radiography Student

Lateral Aspect Of The Scapula Body Anatomy Muscle Anatomy Scapula









Posting Komentar untuk "Scap Y Projection"